| HOME PAGE |
 |
|
| HOME PAGE |
 |

|
|
Andy Wuensche andy AT ddlab DOT org |
Visiting research fellow Dept. of Informatics (formerly COGS) School of Science and Technology, University of Sussex
Visiting Professor |
DDLab mirror sites: www.ddlab.org www.sussex.ac.uk/Users/andywu www.sussex.ac.uk/Users/andywu/ddlab.html |

|
|
far left: pencil drawing from the very early days left: automatic computer drawing of the same basin of attraction |
|
latest updates EDD Manual DDLab versions - the X‑rule - 3d‑glider‑guns - Lecture slides - DD‑Life - Beehive‑rule - Spiral‑rule - The DDLab Gallery - Attractor basins - What is DDLab? - Reviews - Registration - Publications - Presentations |
José Manuel Gómez Soto Universal Computation in 2D Cellular Automaton |
|
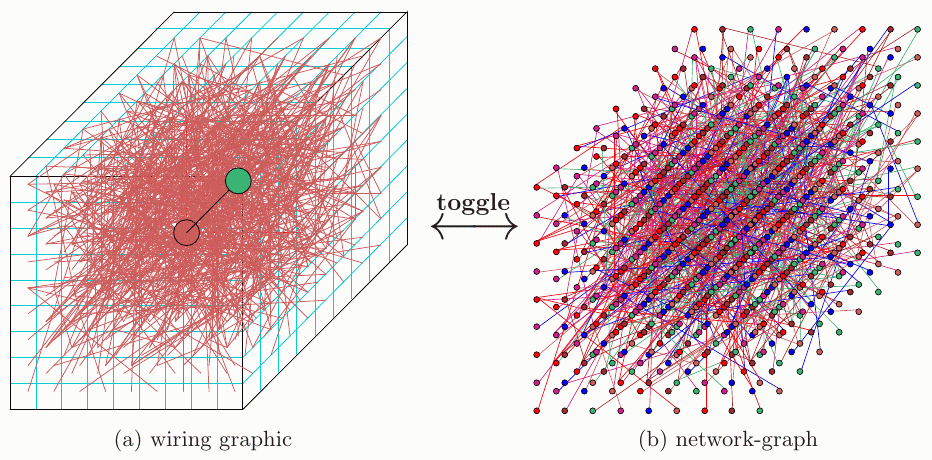
ddlabz13 update January 2025 This Jan 2025 update (following the Sept 2024 update) includes ... a new toggle between the "wiring graphic" and the "interactive-graph", and some improvements and bug fixes, including ...
|

|  |
| updated EDD 2025 | (EDD) Exploring Discrete Dynamics -- updated Second Edition -- The DDlab Manual. This hyperref pdf book corresponds to ddlabz13 Jan 2025. |
 |
|||||
| ddlab_compiled_Jan2025 | compiled ddlabz13, for Linux, Mac, Cygwin, DOS, and readme's.
|
ddlab_code_Jan2025
| source code for ddlabz13, readme's, and Makefiles |
structured archive
|
structured archive of compiles, code, and documentation, | for the latest and all previous versions dating to back to 1995.
unstructured download directory | of compiles, code, and docs, for the latest and
previous versions. Also includes
dd_extra.tar.gz
extra files to supplement DDLab and
fonts for Linux which may be required.
| |
|
Online update 2025: Exploring Discrete Dynamics - Second Edition
The first edition was published in 2011, the second edition in 2016, by Luniver Press, an 8x10 inch 577 page paperback
with color figures, available at
Amazon-UK,
Amazon-USA, and other online book sellers.
back cover quote by Stuart Kauffman More reviews here. |

|
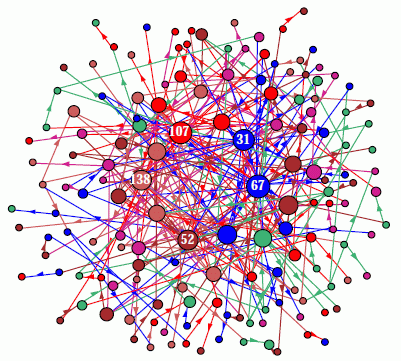
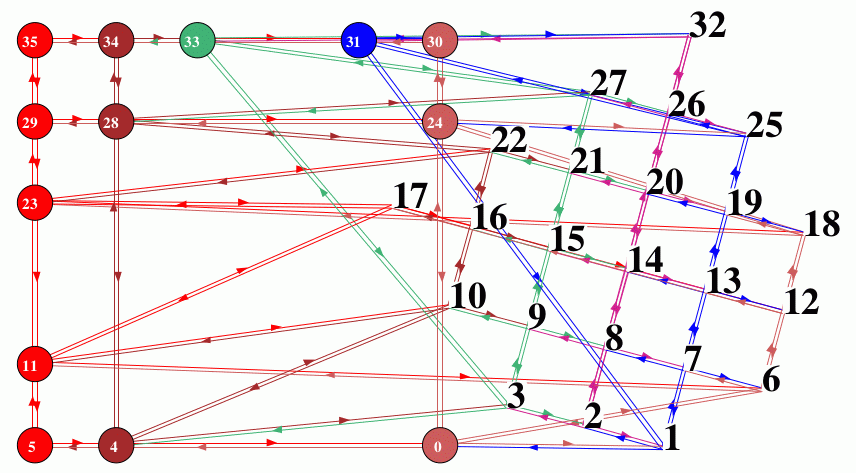 2d Network-graph with a dragged linked fragment on active node 14 |
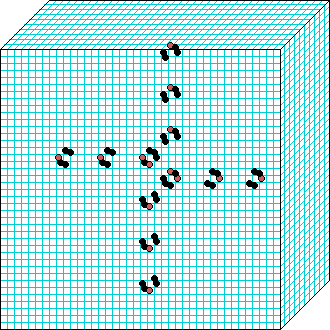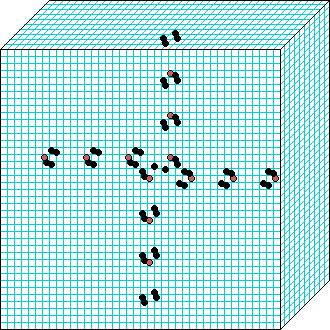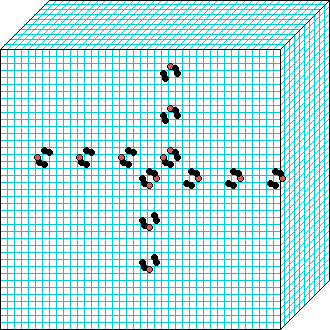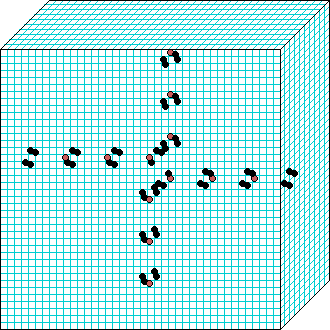 3d glider-gun click to enlarge |
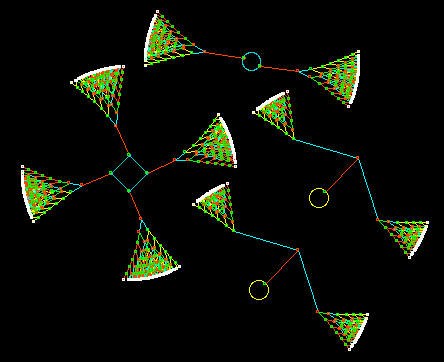
 The Spiral Rule |
 1d CA space-time pattern as a >scrolling tube. The present moment is at the front. |
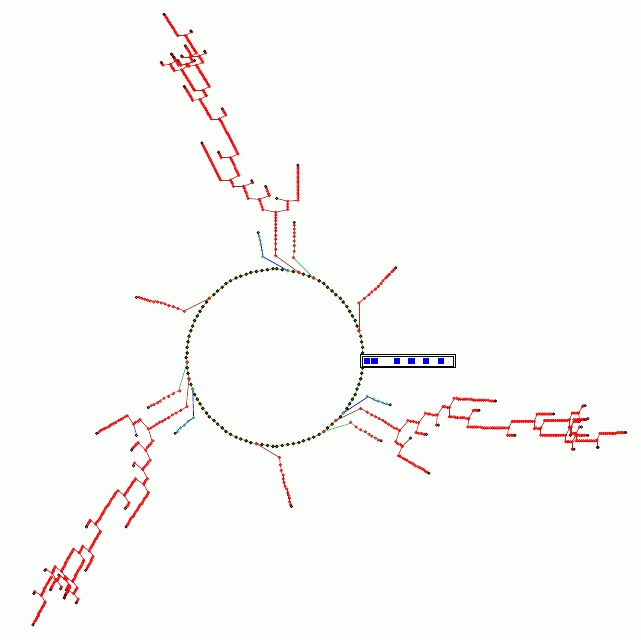
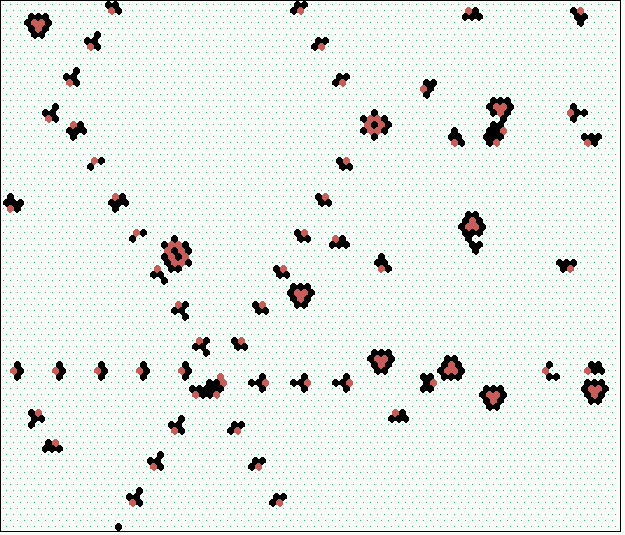
Null Bpoundary Conditions, Basin of attraction field, ECA rule 150, n=11 |
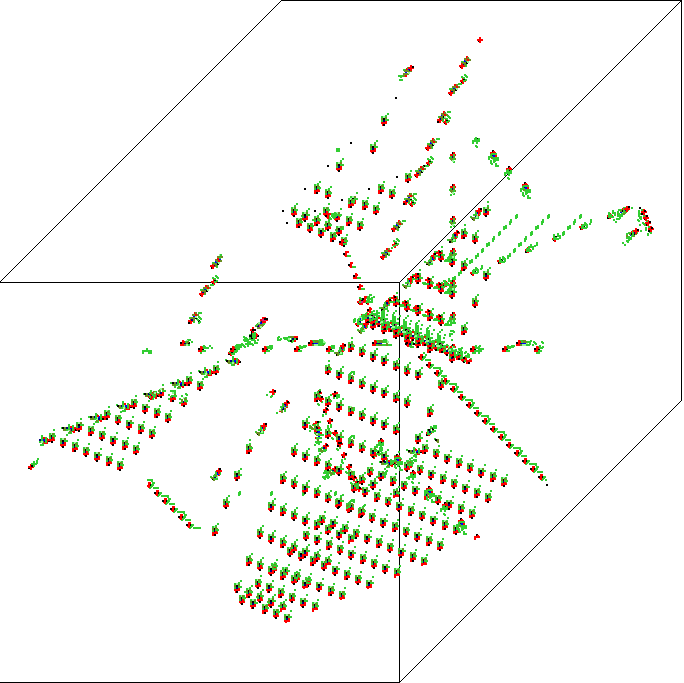 3d 200x200x200 space-time patt- ern. Large sizes are possible in ddlabx09 |
DDLab is free (open source) software under the GNU General Public License.
However, institutional users (commercial or educational) are required to register
and pay a registration fee. Personal users are also encouraged to register.
Registered users will receive a simple instruction to remove the annoying
"UNREGISTERED" banners in DDLab. For registration details, click
HERE.
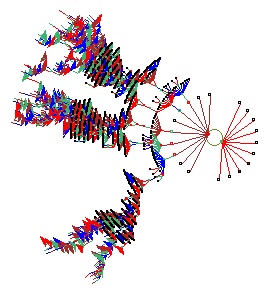
The figure on the right shows a way of representing
a network as a graph which can be rearranged by dragging vertices.
This is a "scale free" RBN, n=150
with a power-law distribution of both k and out-degree. DDLab is interactive graphics software for researching
discrete dynamical networks, relevant to the study of complexity,
emergent phenomena, neural and bio-molecular networks - especially
gene regulatory networks, and any other dynamical process that plays out
across a directed network, where nodes receive inputs from
other nodes.
A discrete dynamical network (DDN) can have arbitrary connections
and heterogeneous rules, and includes Cellular Autamata (CA),
and "Random Boolean Networks" (RBN), where the
"Boolean" atribute is extended to multi-value.
Lattice dimensions can be 1d, 2d (triangular, hex, or square) or 3d.
Many tools and functions are available for creating the network
(its rules and wiring), setting the initial
state, analyzing the dynamics, and amending parameters on-the-fly.
An overview is provided in this
2008 pdf preprint, and the in-depth operating manual "Exploring Discrete Dynamics"
Jan 2025 update.
The program iterates the network forward to display space-time patterns,
and also runs the network "backwards" to generate a pattern's
predecessors and reconstruct its branching sub-tree of all ancestor patterns.
For smaller networks, sub-trees, basins of attraction or the whole basin
of attraction field can be reconstructed and displayed as
directed graphs in real time.
The DDLab
Gallery shows examples.
The DDLab Galleryxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
The DDLab
Gallery
is a collection of DDLab images and graphics, with captions,
illustrating some of DDLab's features up to the time the Gallery was started in Oct 1998.
Later graphics between then and now can be found in updates.
A similar graph is the "attractor jump-graph",
which shows the probability of jumping between basins of attraction
subject to noise. For some examples
click here
Lecture slides
About 80 lecture slides from 2006.
Click here to see the slide pdf
- its a large file so might take a minute.
You may use/copy these slides provided the source is propery referenced.
Attractor Basinsxxxxxxxx
Attractor basins of discrete dynamical networks are objects in
space-time that link network states according to their
transitions. Click
here for a summary of idea.
Access to these objects, depicted as state transition graphs
according to DDLab's graphic conventions, provides insights into complexity,
chaos and emergent phenomena in cellular automata. In less ordered
networks (as well as CA), attractor basins show how a network is able to
categorize its state space, explaining what it is that constitutes
memory in a network.

detail of a basin of attraction of an RBN. Click to enlarge
What is DDLab?
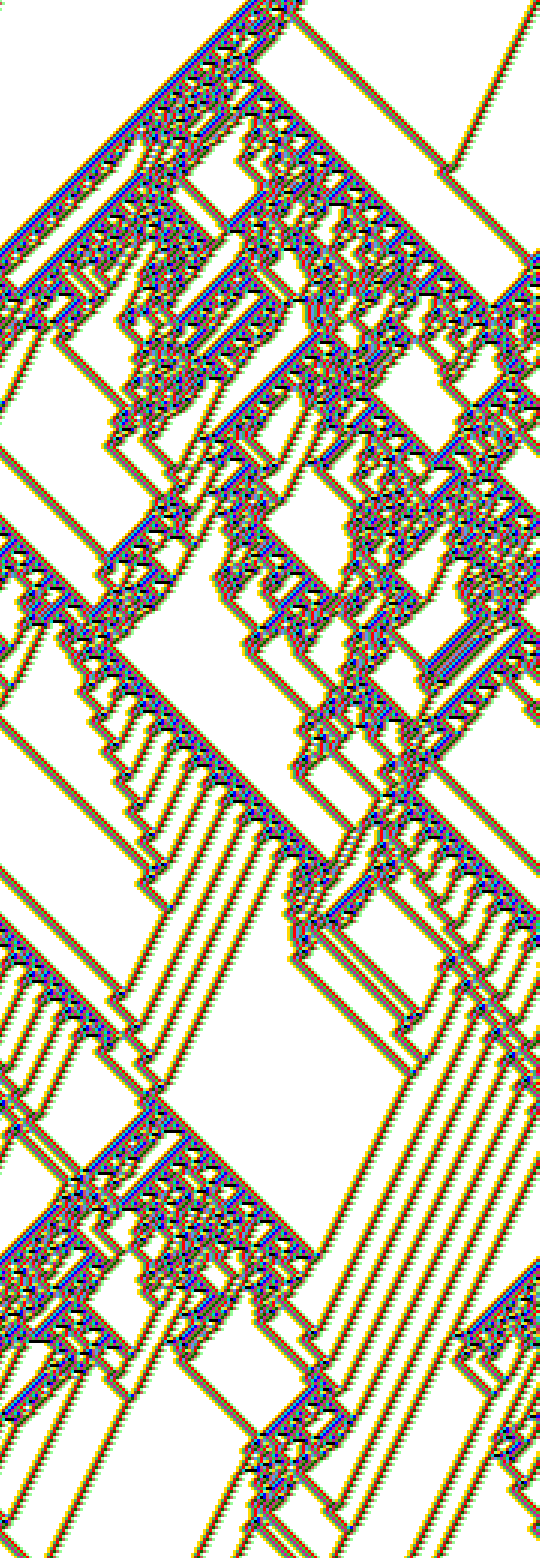
1d scrolling space-time pattern
v2k5 rule 5c6a4d98. Click to enlarge
Reviewsxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Early Reviews of DDLab
Reviews of
"The Global Dynamics of
Cellular Automata"
The entire book has been scanned and is available in
pdf -- 39,09M.
Reviews of
Exploring Discrete Dynamics

DDLab's screen saver -- click to enlarge
Related Publicationsxxxxx
Books and various papers related to DDLab are
listed
here, most are in pdf.
back to the start of DDLab
Last modified: Jan 2025


